Reason to trust

How Our News is Made
Strict editorial policy that focuses on accuracy, relevance, and impartiality
Ad discliamer
Morbi pretium leo et nisl aliquam mollis. Quisque arcu lorem, ultricies quis pellentesque nec, ullamcorper eu odio.
MIT Media Lab blog has published a new paper called “What we learned from designing an academic certificates system on the blockchain” which researches the attributes of using distributed ledger technology with digital certification. For a year, the team of researchers worked on a project to verify digital credentials using the Bitcoin Blockchain and Mozilla Open Badges.
The MIT Researchers say the Bitcoin Blockchain is the ‘most tested and reliable blockchain to date.’
The team of researchers from MIT have released the code to this open source project to make it easier for people to build similar applications. The project was conceived because of the belief in the importance of immutable digital credentials. The paper details a previous post written by J. Philipp Schmidt proposing that the certificate concepts could replicate the days in the past when “journeymen carpenters carried around their books of stamps and references.” Throughout the paper, the authors say they have learned quite a bit about blockchain technology and even the “hype.” MIT Media Labs report recognizes there is a lot of attention aimed at distributed ledger technology but it’s not entirely simple. The MIT blog post written by Juliana Nazaré, J. Philipp Schmidt, and Kim Hamilton Duffy explains:
“One important takeaway for us has been that the blockchain is a lot more complicated than most people make it out to be. Building applications on top of it–which is what we did–is getting easier, but there are still very few people who deeply understand its inner workings (and we don’t consider ourselves part of that group). The blockchain is not a simple solution that will fix everything that is wrong with today’s credentials. But it does offer some possibilities for improving the system we have today–and that’s what we are excited to explore.”
Links to the source code and discussions about the project can be seen here and the team says the certificate architecture is “fairly simple.” The digital certificates framework includes the following repositories Cert-schema, Cert-issuer, and Cert-viewer which work together to broadcast the data into the Bitcoin blockchain. The paper also mentions the Ethereum blockchain saying that when they started the programmable currency was in its infancy and the Bitcoin Blockchain is the “most tested and reliable blockchain to date.”
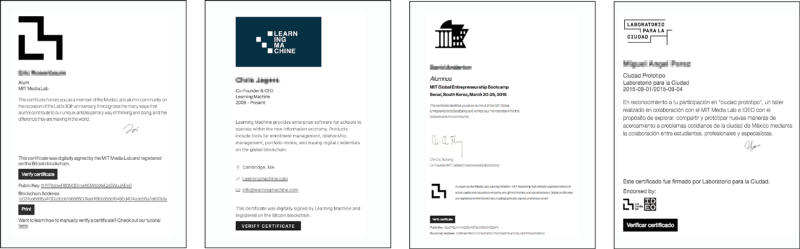
The researchers at MIT also use public/private key cryptography to authenticate issuers and recipients of the digital certification. The application also has a revoking feature to remove a certificate but it is not an actual deletion because the original information can never be deleted from the blockchain. The blog post notes the Bitcoin distributed ledger is open and immutable but the authors recognize people still have a concern for privacy. The report explains:
“Some of our colleagues at MIT are working on systems that will provide more sophisticated ways of managing private data, but these are still in the early development stages. In our current solution, we try to balance obfuscation with usability so that institutions or learners that lack advanced technical sophistication will not be prevented from using the credentials. We do this by hashing the certificate and only placing the hash on the blockchain. If someone wants to verify the validity of a certificate, they need the learner to disclose both the certificate itself and where the hash of the certificate is located on the blockchain.”
The right to curation is an important measure to the authors for people who like to pick and choose what certificates they would like to be publicized. The group says it is entirely up to the curator on how much they would like to share about themselves. For instance with the MIT blockchain verified certification an educator may want to look at a student’s academic records. The teacher could try and search for the students employment certification but “the content of these certificates will be encrypted.” Although the researchers say there are “shortcomings” and they are trying to make traceability harder with future implementations.
The project is currently available for testing the application at the researcher’s new digital authentication MIT Media Lab web site. The creators of the projects say if people are experimenting with this type of technology they should join their GitHub repository. Overall the MIT researchers seem pleased with the work they accomplished and look forward to continuing the project. MIT has a strong influence when it comes to digital currency and blockchain solutions with backing from its very own Digital Currency Initiative. It’s good to see such innovation coming out of the Boston school as they seem to be embracing the subject head on.
Source: MITMediaLab
Images: MITMediaLab & NewsBTC


















